Scientists have used the world’s largest array of seismic sensors to map a deep-Earth area of melting carbon covering 1.8 million km2 (684 000 mi2).
The enormous reservoir is situated under the Western US, 350km beneath the Earth’s surface, challenges accepted understanding of how much carbon the Earth contains… Much more than previously understood.
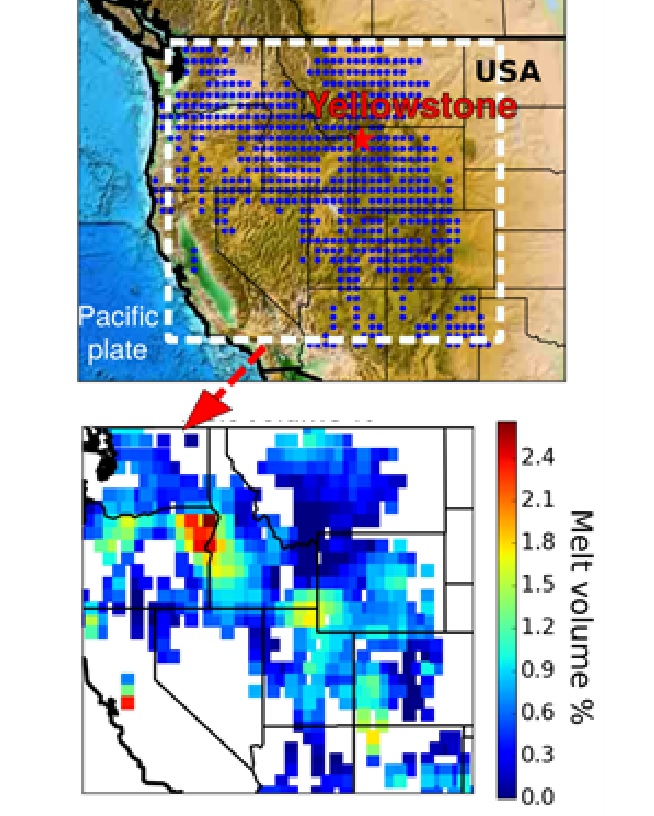
The study used a huge network of 583 seismic sensors that measure the Earth’s vibrations, to create a picture of the area’s deep sub surface. Known as the upper mantle, this section of the Earth’s interior is recognised by its high temperatures where solid carbonates melt, creating very particular seismic patterns.
The scientists explain: “It would be impossible for us to drill far enough down to physically ‘see’ the Earth’s mantle, so using this massive group of sensors we have to paint a picture of it using mathematical equations to interpret what is beneath us. Under the western US is a huge underground partially-molten reservoir of liquid carbonate. It is a result of one of the tectonic plates of the Pacific Ocean forced underneath the western USA, undergoing partial melting thanks to gasses like CO2 and H2O contained in the minerals dissolved in it.”
Scientists now know the amount of CO2 in the Earth’s upper mantle may be up to 100 trillion metric tons. In comparison, the US Environmental Protection Agency estimates the global carbon emission in 2011 was nearly 10 billion metric tons – a tiny amount in comparison.
Climate change consequence
“We might not think of the deep structure of the Earth as linked to climate change above us, but this discovery not only has implications for subterranean mapping but also for our future atmosphere. For example, releasing only 1% of this CO2 into the atmosphere will be the equivalent of burning 2.3 trillion barrels of oil. The existence of such deep reservoirs show how important is the role of deep Earth in the global carbon cycle.”
That’s a pretty creepy discovery, right under the Yellowstone supervolcano!











