A large pockmark field of more than 915 km2 with up to 1,200 pockmarks per square kilometer has been identified in the southeastern North Sea during multibeam bathymetry surveys.
The time of emergence can be confined to 3 months in autumn 2015, suggesting a very dynamic genesis. The gas source and the trigger for the simultaneous outbreak remain speculative. Just scary!
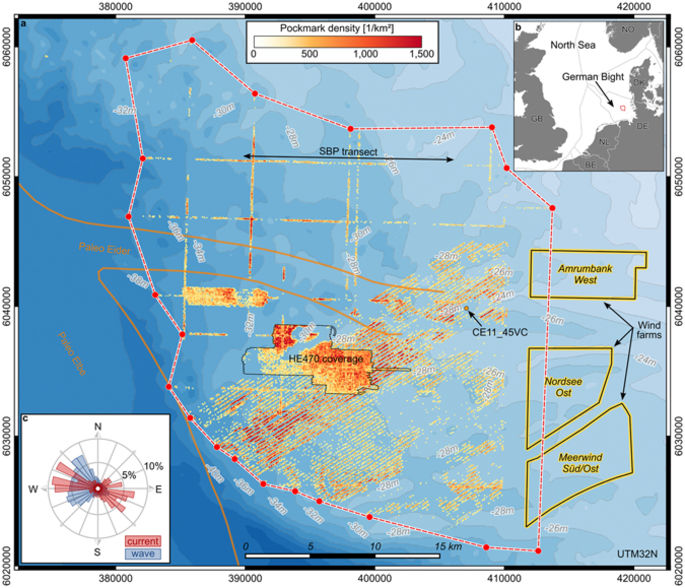
Pockmarks are morphological expressions of vigorous fluid escape from subaqueous sediments.
Subseafloor structures and high methane concentrations of up to 30 μmol/l in sediment pore water samples suggest a source of shallow biogenic methane from the decomposition of postglacial deposits in a paleo river valley.
Storm waves are suggested as the final trigger for the eruption of the gas.
Due to the shallow water depths and energetic conditions at the presumed time of eruption, a large fraction of the released gas must have been emitted to the atmosphere.
Conservative estimates amount to 5 kt of methane, equivalent to 67% of the annual release from the entire North Sea.
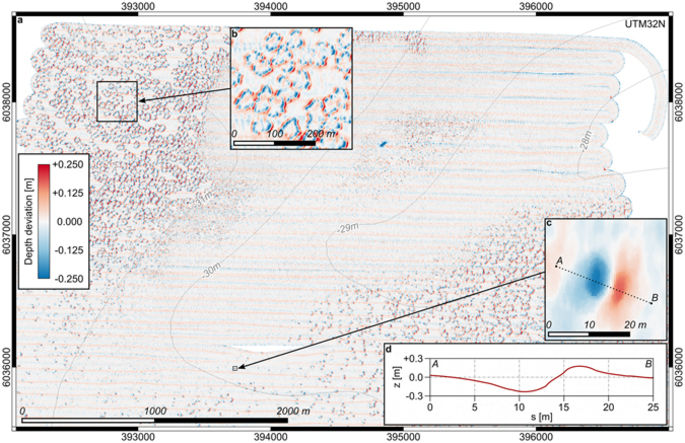
These observations most probably describe a reoccurring phenomenon in shallow shelf seas, which may have been overlooked before because of the transient nature of shallow water bedforms and technology limitations.
Begnning of this year, hundreds of gigantic craters from past catastrophic methane eruptions were found on the sea floor in the Arctic Ocean.