
Scientists in France have created a way to divert lightning strikes using a weather-controlling super laser.
Researchers with the Polytechnic Institute of Paris guided the strikes from thunderclouds to places where they don’t cause damage. The team says the new technique could save power stations, airports, launchpads, and other buildings from disaster.
The system creates a virtual lightning rod, metal conductors that intercept flashes and guide their currents into the ground.
“The findings extend the current understanding of laser physics in the atmosphere and may aid in the development of novel lightning protection strategies,” says corresponding author Dr. Aurelien Houard, according to a statement from SWNS.
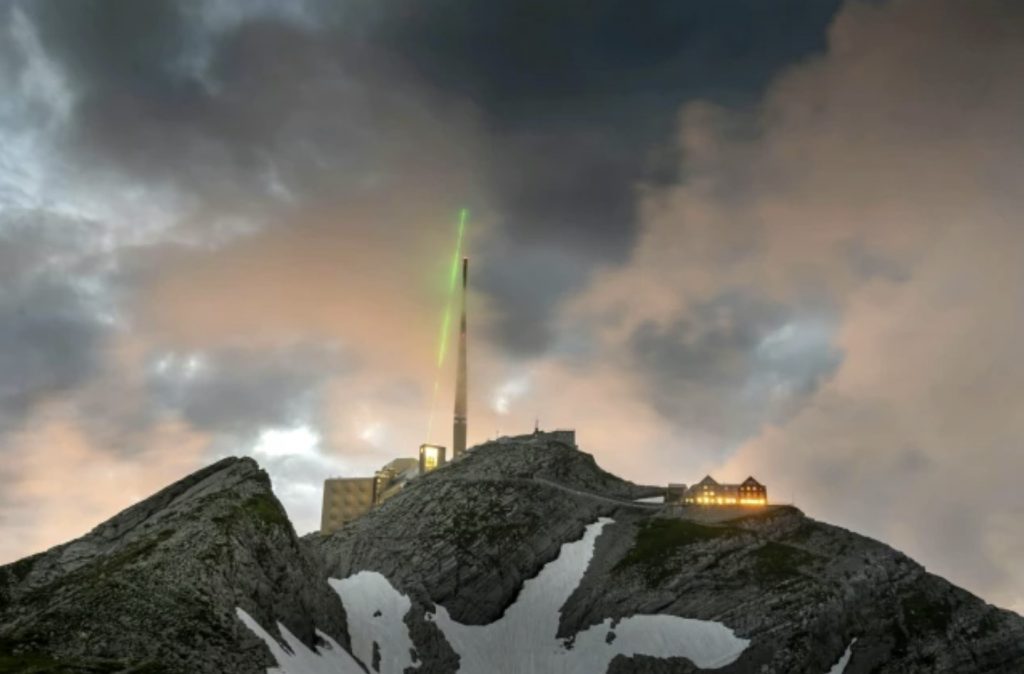
The five-ton device is about the size of a large car and fires up to a thousand pulses per second. The scientists installed it near a telecommunications tower in the Swiss Alps – which is struck by lightning around 100 times a year.
FUNDRAISING: KEEP STRANGESOUNDS ONLINE!… THANK YOU FOR YOUR HELP!
“A powerful laser aimed at the sky can create a virtual lightning rod and divert the path of lightning strikes,” Dr. Houard tells SWNS. “The findings may pave the way for better lightning protection methods for critical infrastructure – such as power stations, airports and launchpads.”
Lightning rods were invented by Benjamin Franklin in 1752 as part of his groundbreaking exploration of electricity, and they’re still in use today. However, installing them is often impractical. They only combat the direct effects of lightning strikes and can cause electromagnetic interference and voltage surges in devices and appliances.
“Acting as a virtual, movable rod, a laser beam directed at the sky could offer an alternative,” Dr. Houard continues.
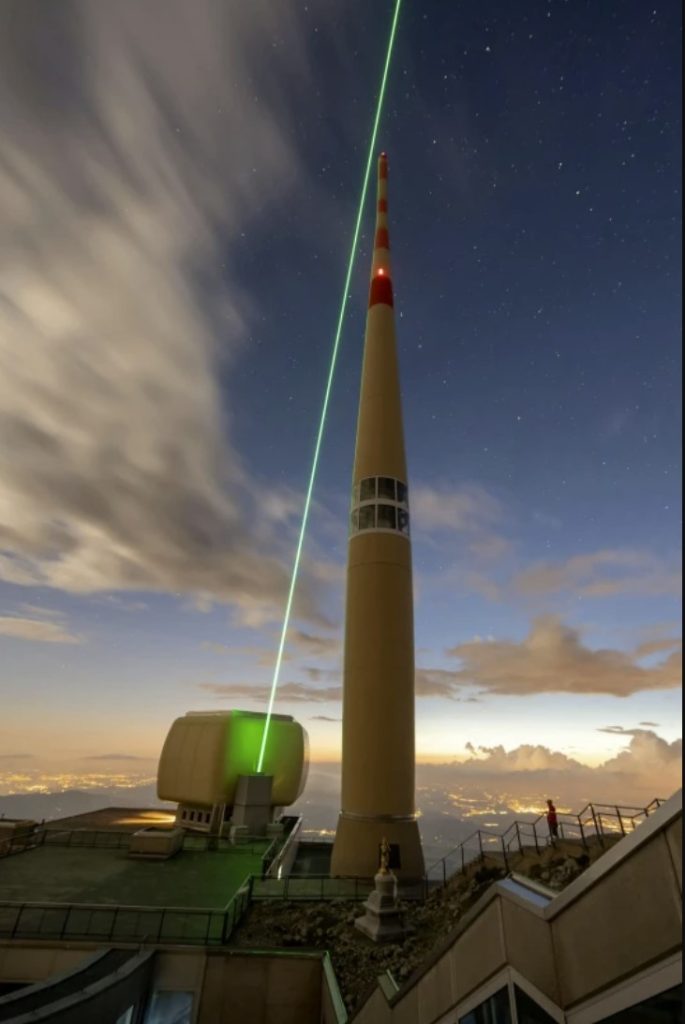

The laser could prevent billions of dollars in damage
The idea of using intense laser pulses to guide lightning strikes has been previously explored in laboratory conditions. However, there weren’t any field tests that previously demonstrated lightning guiding by lasers. Dr. Houard and colleagues carried out a series of experiments last summer on the top of Mount Santis in northeastern Switzerland.
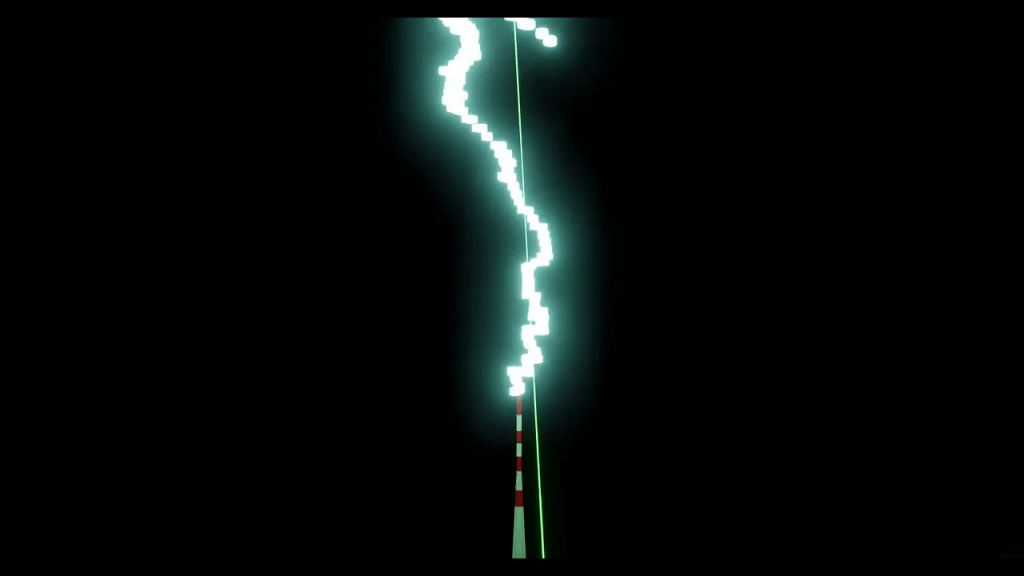
In six hours of operation during thunderstorms, they observed the laser diverting the course of four upward lightning discharges from the 400-foot-tall tower. Results were corroborated using high-frequency electromagnetic waves generated by the lightning to locate the strikes.
“Increased detection of X-ray bursts at the time of the strikes also confirmed successful guiding,” Dr. Houard tells SWNS. “One of the strikes was directly recorded by high-speed cameras and shown to follow the laser path for over 50 meters.”
The trillion-Watt laser described in Nature Photonics is the first of its kind, and one of the most powerful in its class.
FUNDRAISING: KEEP STRANGESOUNDS ONLINE!… THANK YOU FOR YOUR HELP!
Lightning has immense destructive power. It can cause power outages and forest fires, damage electronic systems and infrastructure, and even lead to the injury or death of humans and livestock. The damages it causes amount to billions of dollars every year. With climate change and the consequent rise in the frequency and severity of storms, damages from lightning will probably increase in the future.
Redirecting lightning using lasers would therefore help protect vulnerable sites such as airports, forests, skyscrapers, and power plants. The laser works by generating a long, ionized channel called a laser filament towards the clouds. It acts as a preferential path for the lightning, deviating it away from vulnerable sites.
“By shooting a thousand laser pulses a second into the clouds we can safely discharge the lightning and make the world a little bit safer,” adds co-author Dr. Clemens Herkommer of Trumpf Scientific Lasers.

When are lightning strikes a major concern?
Santis is considered one of Europe’s lightning hotspots, mostly concentrated during peak thunderstorm activity between May and August.
“Lightning has fascinated and terrified humankind since time immemorial,” Dr. Houard says.
“Based on satellite data, the total lightning flash rate worldwide – including cloud-to-ground and cloud lightning – is estimated to be between 40 and 120 flashes per second, causing considerable damage and casualties. The documented number of lightning fatalities is well above 4,000 and lightning damages amount to billions of dollars every year.” [Nature, Study Finds]













Remember when the Georgia Guidestones were demolished? I heard on some report that it was a lightning strike. No proof I guess, as they showed some silver car leaving the scene, and no further info came of that, so no proof on that incident either.
Starting to wonder why not much was said after lightning struck the Floyd mural too.
The main thing both objects had in common was being man-made false idols. Now, this story comes out. Is it possibly a distraction from divine wrath?
the video for the destruction of the GGs clearly showed a type of detonation or bomb at the base of the monument, which toppled only one of the plinths. Then later, the rest was dismantled and carted away. To this day nobody knows who blew the thing up, who was the guy in the getaway car, who then dismantled the rest of it, or where the pieces were taken, and most interestingly of all…no one has asked and no one seems to care. Now I find *that* highly suspicious.
So…. if they stop the lightning strikes, where is all that charge going to go to??? Other side of the world and become even more intensified… Lightning is natures way of losing frictional energy that’s built up in the atmosphere and underground.
This is fantastic.
Wonder if it could be used as energy production.Would need an enormous capacitor.Imagine not only safety but supplemental energy
Off track
I thought of a way to obtain wind power that wouldn’t create the problems we currently face(inconsistent animal strikes death.Changes to air sea travel)It requires windmills to be tethered in the stratosphere.There is a layer where the winds are consistent fairly strong.Its our of the way of most animals sea and air traffic.It would be located near antartica.Three major problems materials to withstand it.Probaly doable.
Transporting the electricity.Not so sure if it’s doable.
Mainly due to the heat generated.
Which is the biggest problem.
Unfortunately all the means to cool, have with it ,a risk if it fails.Either or both a chemical spill or high heat that could melt certain sections of the ice cap.
.
Hmmm, can they have that laser guide some lightning bolts at Davos? Maybe plug in some GPS coordinates to get the ones that ditched the meeting as well?
There are plenty of good uses for this technology that I can think up.
?
Off topic /Snow report:
4 corners area getting heavy winds and big fluffy snowflakes. Just started up. Bagged two rabbits in 24 hours, using JSB Hades 15.8gr. hunting pellet .22./700fps. /approx. 20ft lbs. energy. Very bloody affair.
Animals gorge themselves when snow is inbound I have noticed. My young trees won’t get gnawed on like last year.
May want to feed them rabbits. Continuous meat supply.
I like the rump and back legs. The owls like the gut sack and torso/neck meats.
An hour or so later…
Snow all melted now sun is out. This happens up in the mountains alot.
Yeah, all my shots are headshots. This German Weirhrauch HW98 is such an excellent hunting air rifle. 3 x 9 optic. I never miss. 9/9 over the last 12 months. This last shot was easily 50 yards. Quiet too. Those pellets look like a cheese grater on the tip. Massive cavitation.
A Tsar will do.
What’s that supposed to mean?
Must be an azoz nazi trollwad. Putin will squash you like a cockroach.