An enormous dust cloud has finally hit the United States, after journeying 5,000 miles from the Sahara Desert across the Atlantic Ocean.
The plume darkened the skies in Puerto Rico earlier this week, causing some of the highest atmospheric aerosol concentrations the island had ever seen. By yesterday morning, the cloud had begun to creep over the Gulf Coast. Meteorologists say the hazy skies could last into the weekend.
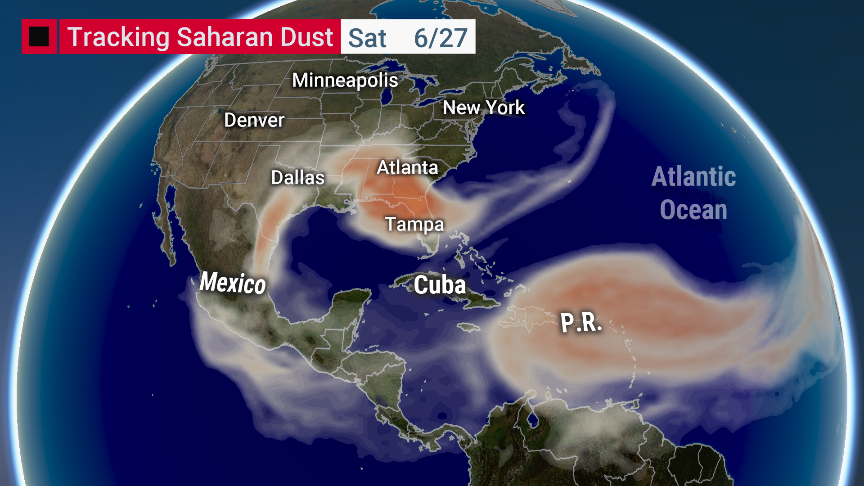
This particular plume is among the most extreme on record, scientists have noted. The thickness of dust particles in the atmosphere is the highest observed in 25 years of satellite measurements.
And its side effects are noticeable wherever it passes: hazy skies and brilliant sunsets, as well as potential respiratory irritation from all the extra dust in the air.
#Dust plume from the Sahara Desert will spread into parts of the U.S. this weekend bringing hazy skies, reduced air quality and beautiful sunrises/sunsets: https://t.co/PQW8IyIb6o pic.twitter.com/gNnuFYNdRd
— The Weather Channel (@weatherchannel) June 26, 2020
“It is an extremely unusual event,” said Joseph Prospero, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Miami, whose research team helped pioneer the study of Saharan dust clouds more than 30 years ago.
In general, Saharan dust plumes actually happen all the time — the Sahara Desert has an endless supply of dust for winds to carry across the Atlantic Ocean. These events just aren’t typically so intense.
SkyEye captured hazy Houston skies thanks to Saharan dust yesterday:
For the time being, it’s unclear whether this particular event is a “meteorological anomaly,” Prospero said, or whether it could be a glimpse into the effects of continued warming.
Here a video from Florida:
Sahara dust rolling into Panama City Beach @spann pic.twitter.com/2OGDtGIFmi
— Nicole Penny ☀ (@npenny2012) June 26, 2020
Saharan dust plumes can have a strong, if temporary, effect on local air quality. They can influence Atlantic hurricane activity. They may even affect tiny organisms in the ocean, which can help suck carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere and into the water.
“There are implications other than the immediately obvious ones,” Prospero said.
The life and death of a Saharan dust plume
The journey begins in the Sahara, a vast expanse of arid land stretching across North Africa. It’s known for its hot, dry conditions — especially in the summer, when surface temperatures can soar well over 110 degrees Fahrenheit.
Hot air rises through the atmosphere as it builds up, sometimes climbing more than 4 miles into the air. As it rises, it carries dust from the surface along with it.
What happens next often depends on local weather conditions. When strong, high winds are present, they can carry the floating dust straight to the coast. There, the dust cloud often encounters a system of westward-moving trade winds.
This hot, dry air gets lifted up over the trade winds, so you develop a layer. We named it in the late 1960s the ‘Saharan air layer.’
The winds then carry this layer of hot, dry, dusty air across the Atlantic Ocean.
As it moves along, the dust cloud can influence its environment in a variety of ways.
Dampening Hurricane Activity
Perhaps most notably, it can dampen hurricane activity in the Atlantic, because the hot, dry Saharan air layer can inhibit the formation of clouds or tear apart any clouds that get sucked into it.
The dust particles themselves can also have a big effect as they can block sunlight from getting through to the Earth’s surface. That can cause sea surface temperatures to temporarily cool, making conditions less favorable for storms.
Moreover, dust particles are also less effective than other kinds of aerosols at helping clouds to form in the atmosphere.
If a dust cloud happens to run into a hurricane that’s already fully formed, the hurricane may actually help transport the dust across the ocean. But otherwise, dust plumes are thought to prevent new hurricanes from forming in the ocean as they move over the water.
Nutrient and bacterial fuel
It’s not the only way dust plumes can affect their surroundings.
Dust contains a variety of minerals and nutrients, such as iron and phosphorus. As dust sprinkles out of the air, these nutrients may help fuel local ecosystems.
For instance, Saharan dust storms are thought to be one important source of phosphorus for plants in the Amazon rainforest. Other experts have suggested that dust plumes may help fertilize the ocean with iron, feeding microorganisms in the water.
That’s not necessarily always a good thing. Some studies have linked dust clouds to toxic bacterial and algal blooms in coastal areas.
As the dust cloud moves over landmasses in the Caribbean and the Americas, it can also significantly alter local air quality. This week’s massive event, for instance, has sparked concerns that the extra pollution could be a threat to people recovering from COVID-19.
Where the dust cloud ultimately ends up may depend on the time of year, Logan noted. A spinning gyre in the Atlantic Ocean helps determine the direction that large masses of air will take.
The gyre often shifts positions in the ocean, depending on the season. In the winter, it typically kicks dust plumes down to South America. In the summer, it sends them hurtling toward North America.
Dust clouds that make it as far as the Americas will eventually run into other weather systems that help break them apart. In the United States, they may get caught up in systems of westerly winds that scatter them over the East Coast.
But it’s clear they can have a substantial influence on their surroundings as long as they persist.
If large dust storms became more common or more intense, for instance, it’s possible they could have a bigger effect on Atlantic hurricanes. Or they might have a bigger influence on ocean ecosystems.
Of course, they have tried to link those Sahara sand storms to climate change but there is no evidences at all (study 1, study 2). So for now, the future of Saharan dust plumes remains unclear. But hey! the one we currently face is unprecedented!
More strange sky phenomena on Strange Sounds and Steve Quayle. Now if you are looking for supplements to increase your healthy lifestyle and sexlife please visit Natural Health Source. [Scientific American]













Well the dust also major causes of Texas and other states and suddenly surge in COVID-20 plus. Texas is closing again. Many states like AZ stopped re openings as well. So Global rest lock-down for all is truth? by Election in USA 80 Percent of Americans will be positive for Corona? Elections will be suspended and help all of us?
Amazing how that much dust can travel so far. A big volcano? Worse, ash is lighter than sand. How about a very limited nuclear attack? If only 10% of China’s Nukes hit the USA, which would be around 40-60 warheads, the radiation would travel across the Atlantic to Europe and Russia. In such an attack, the people in Europe and Western Russia would need to stay in shelters for over a month or more. If Russia attacked with the same limited 40-60 warhead attack, the radiation would blow back over them. A full out attack would poison the earth with radiation for 50 years. Not many people on earth would survive.